DNA/RNA extraction can be divided into two steps: cell lysis and purification. Cell lysis is the process of destroying the cell structure of the sample, thus making the DNA in the sample free in the pyrolysis system. Purification is the process of completely separating DNA from other components in the lysis system, such as protein, salt and other impurities.
Cell lysis process
Conventional lysis solutions contain detergents (such as SDS, Triton X-100, NP-40, Tween 20, etc.) and salts (such as Tris, EDTA, NaCl, etc.).
Functions of detergents.
- Denaturation of protein;
- Destroy the membrane structure;
- Remove proteins that interact with nucleic acids.
Roles of salt
- Provide suitable lysis environment, such as Tris;
- Inhibition of the degradation of nucleic acids by nuclease, such as EDTA;
- To maintain the stability of nucleic acid structures, such as NaCl.
- Protease may be added to the lysis system, and the protein can be digested into small segments by protease, which can promote the separation of DNA and protein, and also facilitate the subsequent purification.
Methods used in DNA purification process
1. Phenol chloroform extraction
This method consists of two steps: The lysis system was repeatedly extracted with phenol chloroform to remove the protein and realize the separation of DNA and protein;
The DNA was precipitated by alcohol to separate nucleic acid from salt.
Phenol chloroform extraction is an effective method to remove protein. However, if the protein content exceeds its saturation, the protein in the pyrolysis system will not be removed at one time, and it needs to be repeatedly extracted, and each extraction will lead to the loss of nucleic acid.
The biggest advantage of phenol chloroform extraction is its low cost and low requirement of experimental conditions.
2. High salt precipitation method
High salt precipitation method is a variant of phenol chloroform extraction method, which omits the trouble of phenol chloroform extraction operation, and almost overcomes all the shortcomings of phenol chloroform extraction method, but the purity of DNA is not stable enough.
3. Centrifugation column purification
This method uses some solid medium, under some specific conditions, to selectively adsorb nucleic acid, but not protein and salt, to achieve the separation of nucleic acid, protein and salt. It is a widely used method for extraction kits nowadays. This method is less affected by human factors and has high stability when exrtacting DNA.
The disadvantage of this method is that when the sample is excessive, it needs to be centrifuged repeatedly, and the extraction efficiency of the sample is low.
4. Magnetic Silica beads method
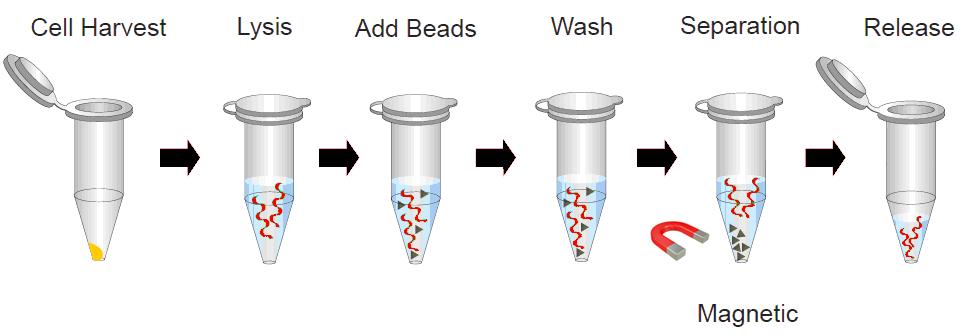
In this method, the purification medium is coated on the surface of magnetic beads. Through the adsorption of DNA by the medium, the DNA is attached to the magnetic beads and moved directionally under the action of external magnetic field, so as to achieve the purpose of separating nucleic acid from other substances.
Compared with other purification methods, the magnetic silica bead method has incomparable advantages.
The extraction sensitivity is high (only a small amount of sample is needed);
The purity of purification is high (the nucleic acid can be completely separated from impurities);
The yield of extraction was high (500 μ g DNA per mg magnetic beads);
The separation speed is fast (magnetic separation only takes a few seconds);
Automatic operation (through the machine to complete the operation process automatically, without manpower);
High throughput extraction (hundreds of samples can be extracted simultaneously);
Non toxic, harmless and pollution-free (the reagent does not contain any toxic substances).
